Strike! Innovation is on strike!
Many years back to sell newspapers, sensational headlines were conceived to get immediate attention so people would buy the paper. It went like this “Strike! Innovation is on strike! Read all about it” Today innovation is actually on strike! Just take a look at this:
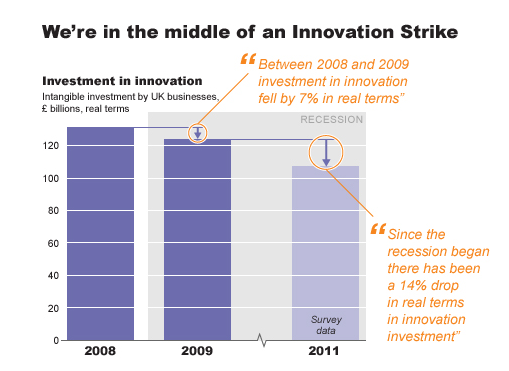
A strike of declining investment, of a lack of confidence, of not sharing in the belief innovation offers a solution to our continued problems of wealth creation, of economic growth, of galvanizing society.
So for many, innovation is actually on strike, we are not investing as we should according to a series of reports and analysis, focusing specifically on the UK economy, sponsored by Nesta. Nesta is the UK’s innovation foundation and they help people and organisations bring great ideas to life.
They do this by providing investments and grants and mobilising research, networks and skills. They operate independently but are very central in shaping innovation thinking.

You can “read all about it” through these links offered, firstly an Executive Summary and the downloading the full report from their site.
