I gaze through unbelieving eyes at the continued rise of unemployed in Europe. Unemployment in the Eurozone has reached another record high with the seasonally-adjusted rate for April 2013 going to 12.2%, up from 12.1% the month before according to the European Commission’s statistics office, Eurostat: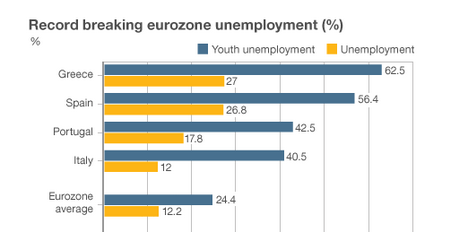 An extra 95,000 people were out of work in the 17 countries that use the Euro, taking the total to 19.38 million. Both Greece and Spain have jobless rates above 25%. The lowest unemployment rate is in Austria at 4.9%.
An extra 95,000 people were out of work in the 17 countries that use the Euro, taking the total to 19.38 million. Both Greece and Spain have jobless rates above 25%. The lowest unemployment rate is in Austria at 4.9%.
It seems never-ending.
Youth unemployment remains a particular concern; you simply have to wonder what we are storing up in the longer term with this situation. Can the youth ever catch up, can our society as it is positioned give them the opportunities to turn today’s grim world into a world of optimism and contentment, or is it a lost generation? In April, 3.6 million people under the age of 25 were out of work in the Eurozone, which translated to an unemployment rate of 24.4%.
Why does this issue of growing unemployment seem to be drowned out by events that seem important on the day but realistically pale in their significance against something as damaging as this present crisis?
Examples of persistent economic and social challenges
We are facing significant society challenges. These include declining Economic competitiveness, deepening Social inequalities, rising Mental ill-health, increasing Crime and social disorder and we see growing Alcohol and drug abuse, to name some of the issues being increasingly tackled as part of the consequences of these tough economic and social times.
We must increasingly recognise that the cost of deferring concerted action to confront these growing set of social challenges is beginning to rise – and could easily outpace our ability to respond.
Can we afford to wait? There are so many pressing questions. Continue reading “Breaking out of the current economic dilemma needs radical innovation”
 The issue of “where does innovation fit?” is one of the most difficult ones to address in many organizations. It seems to fit uncomfortably for many.
The issue of “where does innovation fit?” is one of the most difficult ones to address in many organizations. It seems to fit uncomfortably for many.
